Лидер продаж 200 ватт модифицированный синусоидальный инвертор постоянного тока в переменный ток автомобильный с
- Категории: Inverters >>>
- Поставщик: Guangzhou,Teaimei,Trade,Development,Co.,Ltd.
Поделиться:
Описание и отзывы
Характеристики
Product Description
Product name: | 200W modified sine wave inverter with USB | ||||||
Max continuous power: | 200 watt | ||||||
Peak Load Power Rate: | 400 watt | ||||||
NO load current draw: | <0.4A | ||||||
Input DC voltage Range: | DC9.7V-15V / 20-30VDC | ||||||
Output Voltage Range: | AC110/220V+/-5% | ||||||
Output Frequency Range: | 60/50Hz+/-3Hz | ||||||
Max Outer Temperature: | < 65°C | ||||||
Max Power Efficiency: | > 85% | ||||||
High Voltage Cut Off: | 14.5V-15.5V | ||||||
Low Voltage Alarm Level: | No | ||||||
Low Voltage Cut Off Level: | DC 9.7V+/-0.3 | ||||||
Overload &Short-circuit Protection: | Yes | ||||||
Input Voltage: | DC 12V | ||||||
Output waveform: | Modified sine wave | ||||||
Cooling: | Fan | ||||||
Product Size: | 106*95*55MM | ||||||
Packing size(20pcs/ctn): | 61*25.5*26CM | ||||||
N.W: | 0.36kg | ||||||
G.W: | 0.42kg | ||||||
Application: | Car, home | ||||||
Certification: | CE, RoHS | ||||||
Warranty: | One year | ||||||
Details Images



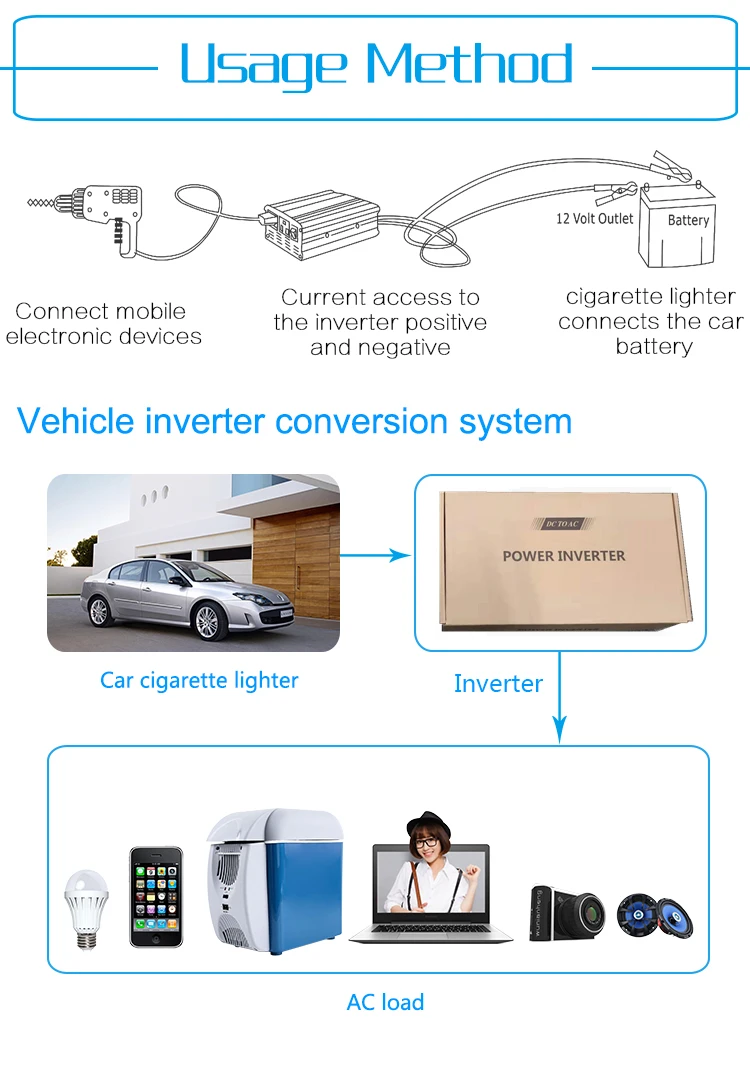
Product Usage
Related Products
Company Introduction
Guangzhou Teaimei Trade Development Company Limited is a professional manufacturer of power inverter, solar controller, dc converter in Guangzhou, China. With constant investments into designs, we can keep our products always meet different demand from market. Good quality and service is our culture!




FAQ
Q1. What is inverter?
A: Inverter is an electronic equipment that turn 12v/24v/48v dc into 110v/220v ac.
Q2. How many kinds of output wave form for inverters?
A: Two kinds. Pure sine wave and modified sine wave. Pure sine wave inverter could provide high quality AC and carry various
loads, while it requires high tech and high cost. Modified sine wave inverter load poorly not carrying inductive load, but the
price is moderate.
Q3. How do we equip an appropriate inverter for battery?
A: Take a battery with 12V/50AH as an example. Power equal current plus voltage then we know the power of battery is 600W.
12V*50A=600W. So we can choose a 600W power inverter according this theoretical value.
Q4. How long can I operate my inverter?
A: The runtime (i.e., amount of time that the inverter will power connected electronics) depends on the amount of battery power
available and the load that it is supporting. In general, as you increase the load (e.g., plug in more equipment) your runtime
will decrease. However, you can attach more batteries to extend the runtime. There is no limit to the number of batteries that can
be connected.
Q5. What's the difference between an inverter and inverter/charger?
A: An inverter simply converts DC (battery) power into AC power and then passes it along to connected equipment. An
inverter/charger does the same thing, except that it is connected to an AC power source to continuously charge the attached
batteries when AC utility power is available. In the case of a power outage, the inverter will automatically switch to battery
power to provide power to connected equipment.
A: Inverter is an electronic equipment that turn 12v/24v/48v dc into 110v/220v ac.
Q2. How many kinds of output wave form for inverters?
A: Two kinds. Pure sine wave and modified sine wave. Pure sine wave inverter could provide high quality AC and carry various
loads, while it requires high tech and high cost. Modified sine wave inverter load poorly not carrying inductive load, but the
price is moderate.
Q3. How do we equip an appropriate inverter for battery?
A: Take a battery with 12V/50AH as an example. Power equal current plus voltage then we know the power of battery is 600W.
12V*50A=600W. So we can choose a 600W power inverter according this theoretical value.
Q4. How long can I operate my inverter?
A: The runtime (i.e., amount of time that the inverter will power connected electronics) depends on the amount of battery power
available and the load that it is supporting. In general, as you increase the load (e.g., plug in more equipment) your runtime
will decrease. However, you can attach more batteries to extend the runtime. There is no limit to the number of batteries that can
be connected.
Q5. What's the difference between an inverter and inverter/charger?
A: An inverter simply converts DC (battery) power into AC power and then passes it along to connected equipment. An
inverter/charger does the same thing, except that it is connected to an AC power source to continuously charge the attached
batteries when AC utility power is available. In the case of a power outage, the inverter will automatically switch to battery
power to provide power to connected equipment.
Contact Way























